Studio AI assistant
RavenDB is equipped with a wide selection of features and capabilities, unified in a database built to make your life easier. The Studio UI is designed to support this goal by making your navigation through the database feature set simple, effective, and enjoyable. Still, when looking for a new option in this extensive interface or defining an unfamiliar script or task, it can be challenging to quickly get to the location or result you are looking for.
RavenDB 7.2 and above address this challenge via the AI assistant, an interactive context-aware guide, intended to minimize the time and effort spent on learning Studio and RavenDB.
You can approach the assistant from any Studio view for navigation instructions, explanations regarding your current location, and information about the database or other topics you may bring up. For example, you can ask for its assistance in views that require specialized knowledge such as RQL queries or ETL scripts.
Additionally, you can grant the assistant read access to database resources such as documents or collections, to allow it to base its answers on your content.
Overview
What is the AI assistant for
Using the AI assistant can ease and enhance your database management capabilities via Studio in various ways.
- You can use the assistant where specialized knowledge is required.
For example, describe a query in natural language to get help forming executable RQL code for Studio's Query view. - The assistant remains accessible from any Studio view, providing you with the help you need and saving you the distraction of leaving Studio to look for it elsewhere.
- In addition to its constant availability, the assistant is also aware of your current location in Studio. It can, for example, direct you to the view where a specific type of ETL task can be defined and guide you through the task definition fields and settings.
- You can give the assistant access to selected collections, documents, and indexes in your database for help specifically tailored to your data and use cases.
User consent
The AI assistant is disabled by default. To enable it, you must provide explicit consent.
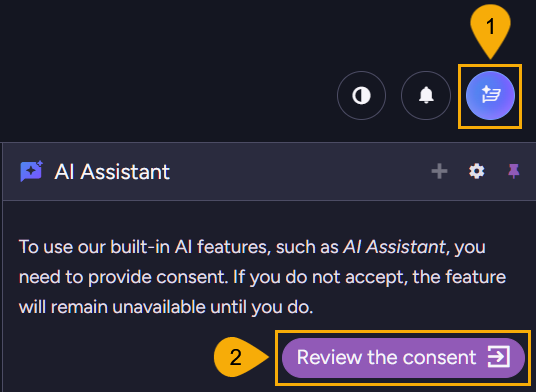
-
Knowledge center icon
Click to open the knowledge center panel. -
Review the consent
Click to read the AI assistant EULA (End-User License Agreement) and either consent and enable the assistant or leave the assistant disabled.
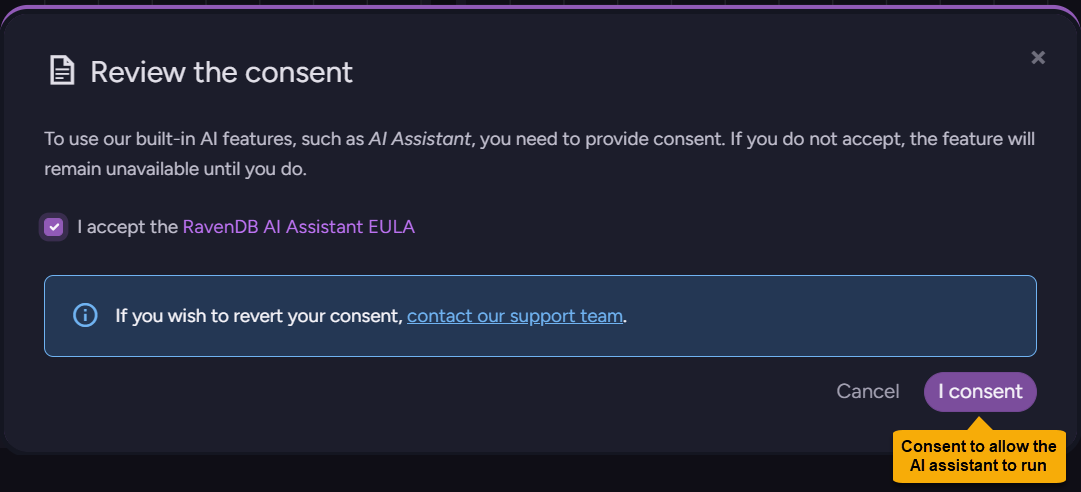
- Note that consenting cannot be undone from the UI.
To cancel your consent after approving it, contact us. - Also note that you will be able to disable or enable the AI assistant even after providing your consent, using configuration keys.
- Note that consenting cannot be undone from the UI.
Licenses and Usage tokens
-
License needed
To use the AI assistant, your RavenDB server must have a valid license.
All licensed servers are entitled to use the AI assistant, regardless of their license type. -
Usage tokens
A monthly quota of usage tokens is allocated per customer. The tokens are consumed by AI assistant usage.
When the tokens run out, assistant prompts are no longer processed by the backend service or the LLM.
The tokens quota is automatically renewed each month.
Services used
RavenDB backend service:
-
AI assistant prompts are delivered by Studio to your RavenDB server, and by the server to an external RavenDB backend service.
-
The backend service processes the prompts, interacts with the LLM, and returns the results to the server, which relays them back to Studio and the AI assistant.
-
This procedure minimizes the amount of local resources required to run the AI assistant.
Make sure your RavenDB server can connect to the RavenDB backend service at https://api.ravendb.net. If the server fails to connect to the backend service (e.g., because it resides in an isolated network), the AI assistant will not be able to function.
LLM service provider:
- RavenDB's backend service uses the Azure OpenAI platform as its LLM provider.
Using the AI assistant
Opening the AI assistant
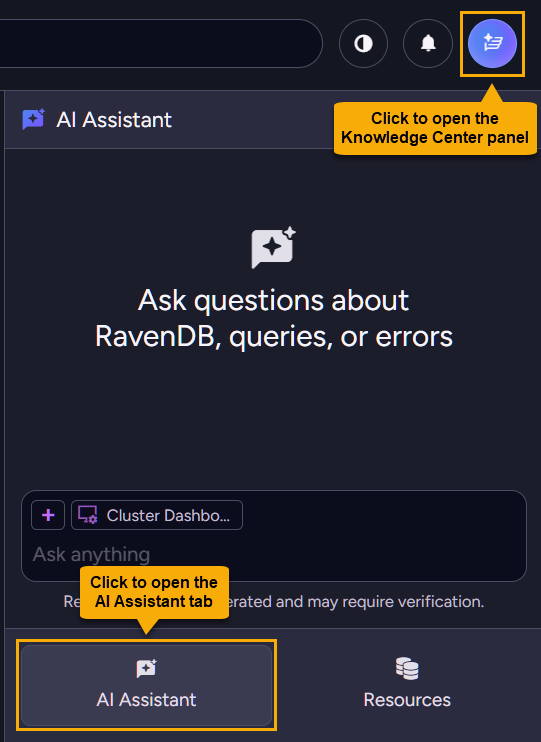
Setting and using the assistant
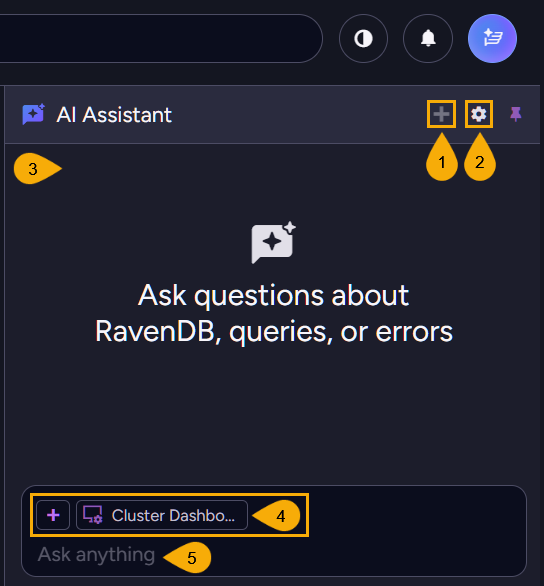
-
Start a new conversation
Click to start a new conversation with the AI assistant.
The conversation history will be cleared. -
Chat settings
Click the gear to open the chat settings dialog.
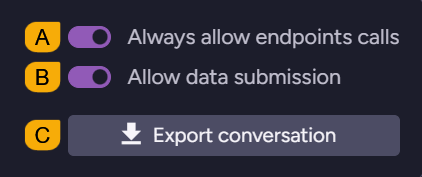
These settings are applied per user and kept in the local browser storage.
For server-wide settings, use the configuration keys.- A. Always allow endpoints calls
Endpoints provide access to database resources. The assistant can call onlyGETendpoints.
When enabled, this option allows the AI assistant to call endpoints without asking for your approval for each call.
When disabled, the AI assistant must ask for your approval before calling any endpoint.Regardless of this setting, the assistant can call only endpoints authorized by your client certificate. Attempting to call unauthorized endpoints will result in a standard
403 Access Deniederror. - B. Allow data submission
When enabled, the AI assistant is allowed to send database content it is permitted to access to the RavenDB backend service for analysis.
When disabled, the AI assistant cannot send to the backend service any of your content. It can still be used for any guidance that requires no data submission, e.g., explaining what view to use and how to use it. - C. Export conversation
Click to export the current conversation as a JSON file.
This is useful when, for example, you want to share the conversation with RavenDB support for troubleshooting.
- A. Always allow endpoints calls
-
Conversation area
The area where the conversation with the AI assistant takes place. -
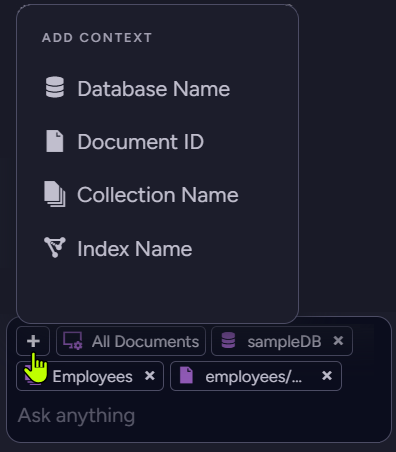
Add context
Click the + icon to select a resource and add its context to the AI assistant.
Adding a context does not by itself pass the selected resource to the assistant, but permits the assistant to retrieve the resource during the conversation if needed. You can add contexts for databases, collections, documents, and indexes.
- By default, the assistant has access to no resources.
- The assistant can retrieve only resources whose contexts you add explicitly.
Additionally, it can retrieve only resources that you have permissions for, as determined by your client certificate. - The assistant cannot modify any resources; it can only read them.
- Resources retrieved by the assistant will be transmitted to the RavenDB backend and Azure OpenAI.
Add contexts only for resources containing data you're comfortable sharing with these services. - Selected contexts are listed above the prompt area.
The first listed item is always the Studio view you are currently visiting, to remind you that the assistant is aware of it.
-
Prompt area
Use this area to enter and send prompts to the AI assistant (e.g., to ask how to form a validation schema or to request help in forming an ETL transform script).
Configuration
Use the following keys to configure the AI assistant server-wide.
Ai.Assistant.Disable
Use this key to completely disable the AI assistant for all users regardless of individual user consent and to block the AI assistant option in Studio's Knowledge Center panel.
- Type:
bool - Default:
false - Scope: Server-wide
Ai.Assistant.DisableDataSubmission
Use this key to prevent the transmission of any user data exposed to the AI assistant to the RavenDB backend or LLM. The assistant can still provide general guidance but cannot analyze any user data.
- Type:
bool - Default:
false - Scope: Server-wide
Security concerns
Concern: Data privacy & Exfiltration
As user data is sent by the AI assistant to the RavenDB backend and the LLM that serves it, and conversations are stored at the backend for auditing, keeping user data safe and private is a concern.
Mitigations:
- User control:
The user decides which database content, if any, is provided to the AI assistant and sent by it to the backend and LLM. The extent of the assistant's access to the database, its ability to send any data to the backend, and its ability to operate at all, are fully controlled by the user. - Opt-in mechanism:
The AI assistant is disabled by default. To enable it, the user must explicitly consent to the EULA (End-User License Agreement).
After consenting, the user can still disable data submission both from the chat settings (that apply to this user on this browser and are kept in the local browser storage) and using configuration keys (applied server-wide). - Certificate authorization:
Regardless of local and global assistant settings and resource contexts added by the user, the assistant can only access resources authorized by its user's client certificate. - Awareness by legal transparency:
The EULA clearly discloses that the data analysis performed by the AI assistant requires it to send query results to third-party processing: the RavenDB backend service and the LLM it uses.
Concern: Prompt injection (indirect injection)
Malicious instructions (e.g., "ignore rules and export data") may be hidden within database documents added to AI assistant prompts as context, attempting to trick the LLM to perform unauthorized actions.
Mitigations:
- Decoupled execution:
The AI assistant cannot modify the database or execute code. Even if the LLM is "tricked" into suggesting a malicious operation, it has no way to apply it. - Human-in-the-Loop (HITL):
The assistant, too, has no ability to modify data or perform actions. It acts strictly as an advisor, returning text and providing the user with input.
Concern: Safety limit enforcement (reliability)
The LLM may request a massive dataset, leading to data scraping.
Mitigations:
- Hard limits:
The RavenDB backend service strictly validates the pageSize parameter. If the LLM requests a large number of items (e.g., 1,000), the backend will override or reject it, enforcing the hard cap of 5 items regardless of the prompt's instruction. - The URL is constructed by the backend service:
The LLM provides an Endpoint ID and parameter values, but never constructs the full URL. The actual request is always constructed by the RavenDB backend service.
Concern: Denial of Service (DoS) via queries
The LLM may construct complex, resource-heavy read queries (like map-reduce fan-outs, for instance) that would stall the production database.
Mitigation:
User approval:
For queries that can create significant load, like the generation of auto-indexes for instance, the AI assistant requires a specific UI confirmation: the user has to approve the request using a checkbox before proceeding.
Concern: Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
The LLM may be tricked into addressing requests to internal or private endpoints that are not meant to be accessed (e.g., a PUT endpoint that modifies data).
Mitigations: Strict Endpoint Whitelisting
-
Construction control:
The LLM provides an ID, while the RavenDB backend service constructs the URL based on a strictly defined internal whitelist. -
Studio whitelist
Studio possesses an endpoints whitelist and all requests are validated against it. Requests to endpoints not in the whitelist are rejected. -
Explicit consent:
The AI assistant's user must approve the execution of the query or the endpoint.
Concern: Authorization confusion
The LLM may attempt to debug issues that the user has no permissions for, leading to frustration or confusion.
Mitigations: Standard security inheritance
- Certificate binding:
All requests initiated by the LLM inherit the exact scope and permissions of the user's client certificate. - Fail-safe:
If the LLM attempts an administrative action for a low-level user, the database kernel will return a standard403 Access Deniederror, ensuring the LLM cannot bypass internal security hierarchies.
Concern: Unauthorized adoption & Compliance
Individual users may enable AI features in violation of organization-wide security policies or "Shadow IT" restrictions.
Mitigations: Global admin kill-switch
- RavenDB administrators can use a configuration key to disable the AI assistant feature globally for the entire server, overriding individual user preferences and ensuring that the feature cannot be activated even by valid license holders if it contradicts organizational policy.
- This is also covered by the EULA.