Migration: previous-versions breaking changes
-
This page lists breaking changes introduced in RavenDB versions earlier than
7.2.
Each breaking change indicates a behavior change or a function that is no longer available in the specified version. -
Find RavenDB
7.2breaking changes here. -
In this article:
RavenDB 7.0 breaking changes
RavenDB incorporates NLog as its logging system
RavenDB's logging system has changed; the server now incorporates the
NLog logging framework and writes all log data through it.
One of the changes that NLog brings to RavenDB is the richer set
of logging levels, visible right away through Studio's admin-logs view.
Read more about Nlog in the dedicated article.
If you migrate to RavenDB 7.x from an earlier version, please
read the section related to NLog in the migration page.
Removed obsolete properties
The following properties are no longer in use, and have been removed from RavenDB 7.0.
ServerOptions'sAcceptEulaproperty is no longer used,
Please useLicensing.EulaAcceptedinstead.
// Removed
c bool AcceptEula
- The
MemoryInfoResultstruct no longer includes these classes:MemoryUsageIntervals
// Removed
c sealed class MemoryUsageIntervals
MemoryUsageLowHigh
// Removed
c sealed class MemoryUsageLowHigh
RavenDB 6.2 breaking changes
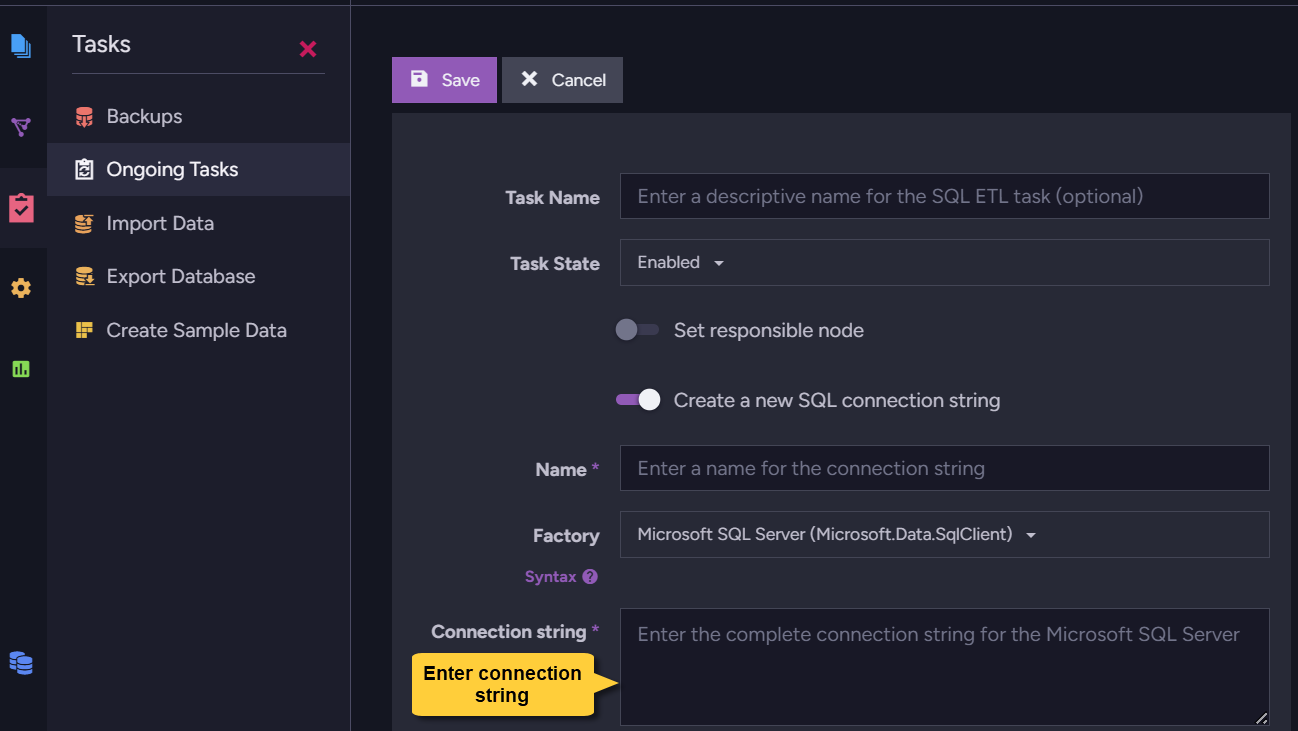
MSSQL connection string requires an Encrypt property
To establish a connection with an MSSQL server via ETL, RavenDB is required
by the Microsoft.Data.SqlClient package it utilizes (which replaces the
deprecated System.Data.SqlClient package we've been using in previous versions)
to include in its connection string an Encrypt property that would determine
whether to encrypt the connection or not.
RavenDB versions preceding 6.2 (down to 6.0.105) added this property
to their connection strings without bothering their users, setting it to
Encrypt=Optional
and leaving the connection unencrypted unless users set it differently on
their own accord.
From RavenDB 6.2 on, we no longer include this property in MSSQL connection
strings and users are required to explicitly choose whether to encrypt the
connection or not.
You can go on using Encrypt=Optional and leave your connection unencrypted, or include Encrypt=Mandatory or Encrypt=Strict in your connection string and provide the server you use with a valid certificate to encrypt the connection.
Provide the connection string using code (like so) or via Studio:
Corax handling of complex JSON objects in static indexes is configurable
The behavior of RavenDB's Corax search engine while
handling complex JSON objects
in static indexes is now configurable using the Indexing.Corax.Static.ComplexFieldIndexingBehavior
configuration option (the handling of auto indexes
remains unchanged).
-
By default,
ComplexFieldIndexingBehavioris set toThrow, instructing the search engine to throw a NotSupportedInCoraxException exception when it encounters a complex field in a static index. -
If you prefer it, you can set
ComplexFieldIndexingBehaviortoSkipto disable the indexing of complex fields without throwing an exception or raising a notification.
- The configuration option will apply only to new static indexes,
created after the release of RavenDB
6.2. It will not affect older indexes. - ComplexFieldIndexingBehavior can be set for a particular index as well as for all indexes.
- Though complex fields cannot be indexed, they can still be stored and projected.
- To search by the contents of a static index's complex field, you can convert
it to a string (using
ToStringon the field value in the index definition). It is recommended, though, to index individual properties of the complex field.
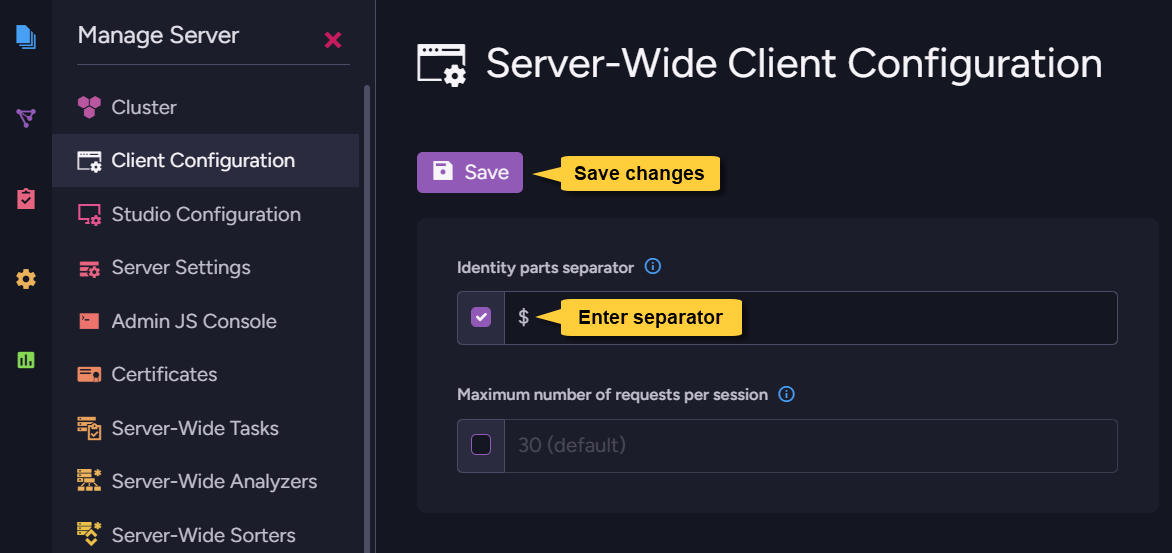
Customizable identifier parts separator
Picking an identifier parts separator allows you to choose which character would be placed as a separator between ID parts when new documents are given their IDs.
This configuration is available in the database level as well as server-wide, but in
versions lower than RavenDB 6.2 its server-wide level wasn't implemented even if
a new separator was selected.
RavenDB 6.2 applies your identifier parts separator selection in the server-wide level
as well. This means that if you selected a separator in a RavenDB version lower than 6.2
and you now migrate to 6.2, your selected separator will become active.
Please be aware of this change and check this setting before migrating.
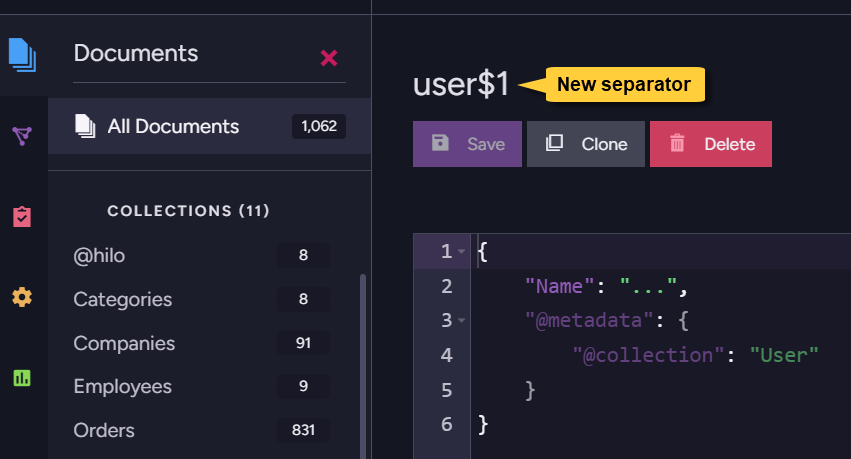
After making this change, creating a new document with the identity prefix |, e.g. user|,
will apply your new separator.
RavenDB 6.0 breaking changes
License keys
License keys for versions lower than 6.0 are not supported by RavenDB 6.0.
If you own a valid license key for RavenDB 5.x or lower, please upgrade it using
the quick online interface described here.
RavenDB for Docker
RavenDB now applies an improved security model, and uses a dedicated user rather than root.
Read more about this change here.
Unsupported sharding features
RavenDB 6.0 introduces sharding.
Server and client features that are currently unavailable in a sharded database (but remain available in regular databases) are listed here.
Graph queries
Graph Queries support,
available in RavenDB versions 4.2 to 5.x, has been removed from the RavenDB 6.x server and client API.
SQL ETL
SQL ETL no longer tolerates errors on Load, load errors are thrown immediately.
This is done to distinguish partial load errors that are used in SQL ETL from, for example, commit errors that may happen during load.
(Prior to this change, the ETL would just advance instead of retrying.)
DateOnly & TimeOnly
DateOnly and TimeOnly types are now supported for every new auto index.
Full-text search with wildcards
Starting with 6.0 we have changed how the Search method handles wildcards when they are included in search terms:
Behavior for versions lower than 6.0:
After the analyzer stripped wildcards from the search term,
RavenDB would attempt to restore the * to their original positions before sending the term to the search engine (Lucene or Corax).
Behavior for 6.0 and up:
Once wildcards are stripped by the analyzer, we no longer add them back before sending the term to the search engine. The search terms sent to the search engine are solely based on the transformations applied by the analyzer used in the index.
Note the different behavior in the following cases:
- When using
RavenStandardAnalyzerorStandardAnalyzerorNGramAnalyzer:
The queried terms in the Search method are processed with theLowerCaseKeywordAnalyzerbefore being sent to the search engine. - When using a custom analyzer:
The queried terms in the Search method are processed according to the custom analyzer's logic. - When using the Exact analyzer:
The queried terms in the Search method remain untouched as produced by the exact analyzer.
When using Corax as the search engine,
this behavior will only apply to indexes that are newly created or have been reset.
See detailed examples in: Searching with wildcards.