Configure remote attachments
-
Storing attachments in a remote storage destination is an optional feature that helps reduce the amount of data stored on the local disk by moving the attachments content to external storage of your choice.
-
To store an attachment in a remote storage destination, you must:
-
When the Remote Attachments feature is enabled:
- RavenDB runs a background task that periodically scans the database for attachments marked for remote upload.
If the upload time for an attachment has passed when the task runs,
the task sends the attachment to the configured remote storage destinations. - Uploading attachments to remote storage runs in the background and does not block other client operations.
- RavenDB runs a background task that periodically scans the database for attachments marked for remote upload.
-
Remote attachments are currently supported only in non-sharded databases.
Attempts to configure remote attachments on sharded databases will throw an exception. -
In this article:
Configuring remote attachments settings - from the Studio
Remote attachments settings
-
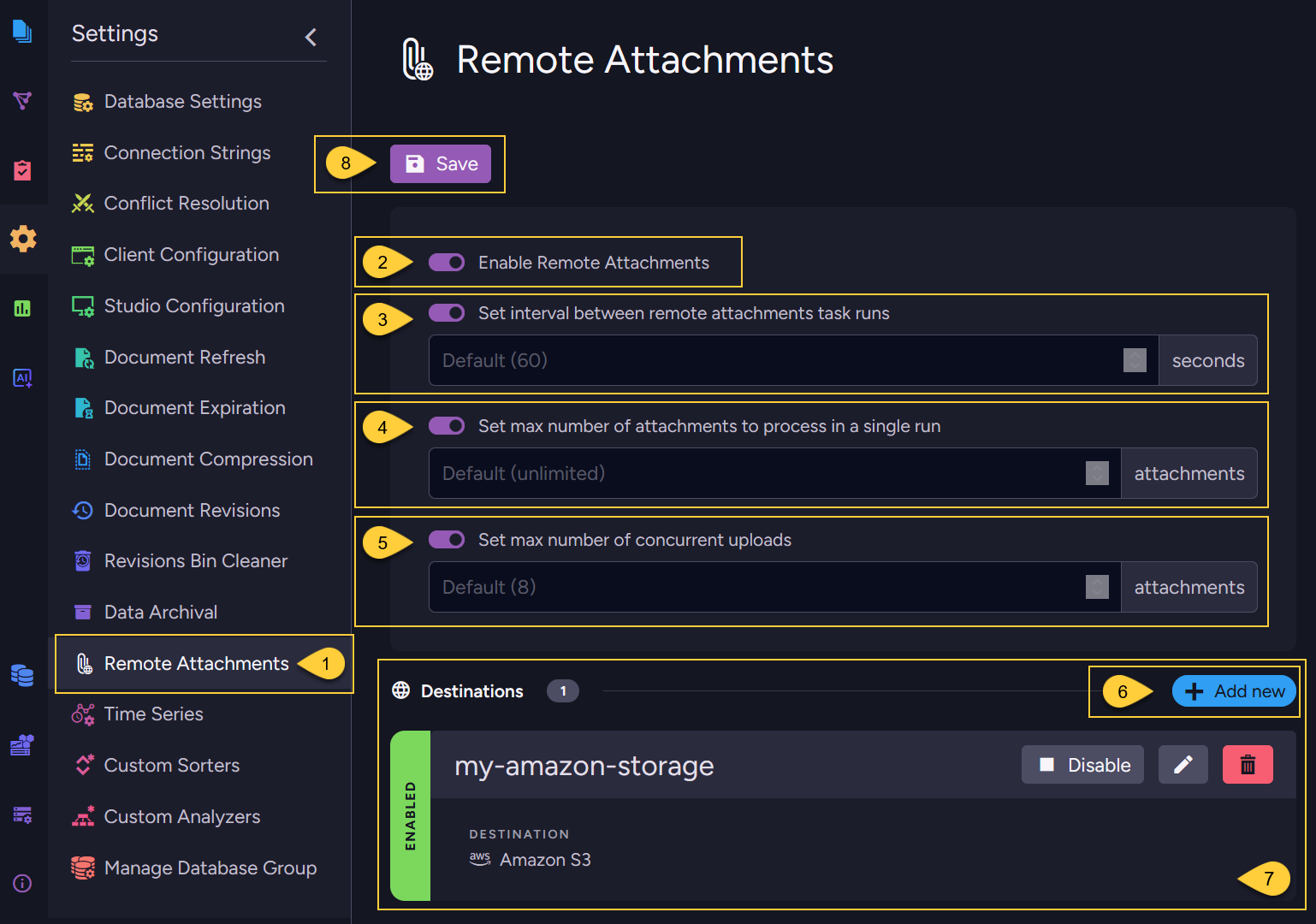
Go to "Settings > Remote Attachments"
-
Enable remote attachments
Toggle ON to enable storing attachments in a remote storage destination. -
Set interval between remote attachments task runs
Toggle ON to specify the delay (in seconds) between background task runs after the task completes the upload of attachments from the previous batch.
Default:60seconds. -
Set max number of attachments to process in a single run
Toggle ON to specify the maximum number of attachments processed in a single background task run.
Default:unlimited. -
Set max number of concurrent uploads
Toggle ON to define the maximum number of attachments that can be uploaded to remote storage concurrently.
Default:8attachments. -
Add new
Click the Add New button to define a new remote storage destination. -
Destinations
All defined destinations will be listed in this section. There is no limit to the number of destinations you can define. -
Save
Click the Save button to save all your changes and apply the configuration.
Destinations
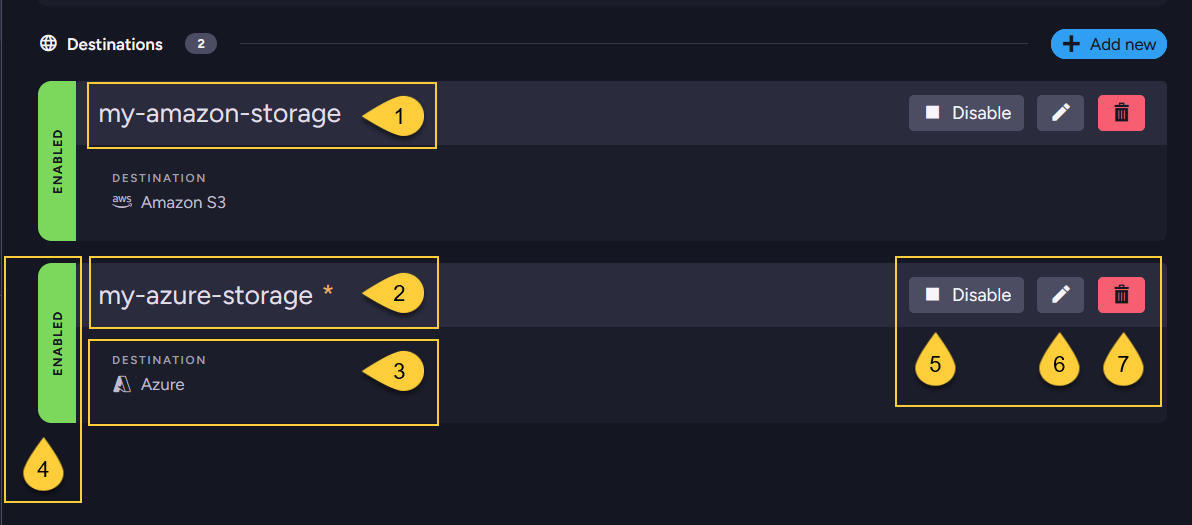
- Destination Identifier
The unique identifier string (case-insensitive) that you have assigned to this remote storage destination. - Unsaved Changes (yellow star)
A yellow star next to the destination's identifier indicates unsaved changes in its configuration. - Remote Storage
The remote storage provider configured for this destination. - Destination Status
When set to Disabled, the destination is ignored by the background task,
and no attachments are uploaded to it, even if their scheduled upload time has passed. - Enable/Disable
Click to toggle the destination's status between Enabled and Disabled. - Edit
Click to modify the configuration settings of this destination. - Delete
Click to remove this destination from the configuration list.
Define destination - Amazon S3 storage
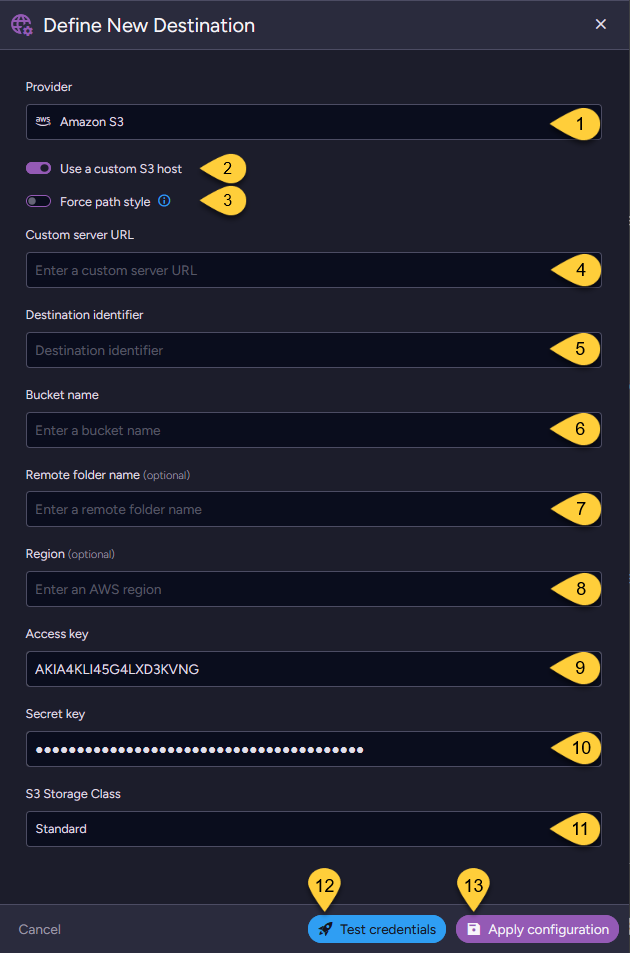
- Provider
Select Amazon S3 as the remote storage provider. - Use a custom S3 host
Toggle ON to specify a custom S3-compatible host other than Amazon's official service. - Force path style
Toggle ON if your custom S3 host requires path-style access instead of virtual-hosted-style URLs.
For example:https://{Server-URL}/{Bucket-Name}instead ofhttps://{Bucket-Name}.{Server-URL}. - Custom server URL
Enter the URL of the custom S3-compatible server (only required if using a custom S3 host).
The URL should include the protocol (http://orhttps://) and may include a port number. - Destination identifier
Enter a unique custom identifier (case-insensitive) for this Amazon S3 destination.
The background task will use this identifier to reference this destination configuration. - Bucket name
Specify the name of the S3 bucket where attachments will be stored.
Bucket names must follow AWS S3 naming rules:- Must be globally unique across all AWS accounts.
- Must be between 3 and 63 characters long.
- Must consist only of lowercase letters, numbers, dots, and hyphens.
- Must begin and end with a letter or number.
- Remote folder name (optional)
Define a folder within the bucket to organize uploaded attachments.
Leave blank to use the root of the bucket. - Region (optional)
Specify the AWS region where the S3 bucket is located (e.g.,us-east-1). - Access key
Provide the AWS access key ID for this S3 bucket. - Secret key
Provide the corresponding AWS secret key for this S3 bucket. - Storage class
Choose an Amazon S3 storage class based on how often you access your data and its retention requirements.
For available options, see S3StorageClass. Default:STANDARD. - Test credentials
Click this option to verify whether the connection to the S3 storage works successfully. - Apply configuration
Click to add this destination to the destination list.
Note: Remember to click the Save button to save all changes.
Define destination - Azure storage
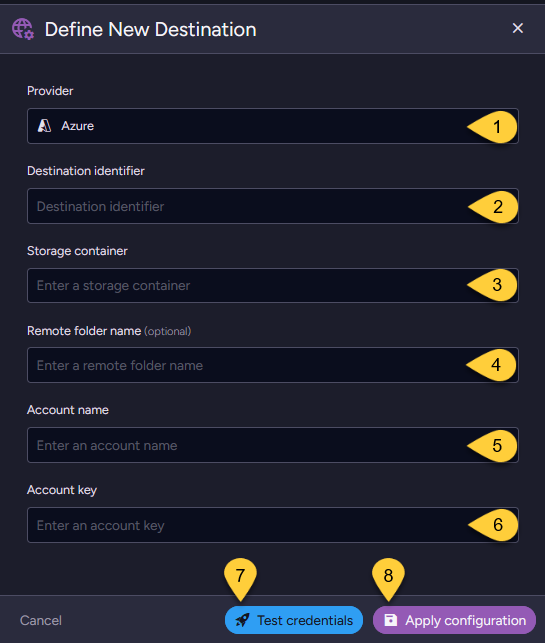
- Provider
Select Azure as the remote storage provider. - Destination identifier
Enter a unique custom identifier (case-insensitive) for this Azure destination.
The background task will use this identifier to reference this destination configuration. - Storage container
Specify the name of the Azure Storage container where attachments will be stored. - Remote folder name (optional)
Define a folder within the storage container to organize uploaded attachments.
Leave blank to use the root of the container. - Account name
Enter the Azure Storage account name. - Account key
Provide the corresponding access key for the Azure Storage account. - Test credentials
Click to verify whether the connection to the Azure storage works successfully. - Apply configuration
Click to add this destination to the destination list.
Note: remember to click the Save button to save all changes.
Configuring remote attachments settings - using the Client API
Configure remote attachments settings
-
Use the
ConfigureRemoteAttachmentsOperationto configure remote attachment settings. -
You can add multiple destinations as needed.
Ensure that each destination has a unique identifier for accurate reference. -
Note:
Configuring remote attachment settings will override any existing configurations on the server.
If you need to add new destinations without losing existing ones,
make sure to Get the current remote attachmets settings first, update it, and then send it back to the server. -
The following example demonstrates how to configure both Amazon S3 and Azure destinations:
- Sync
- Async
// Define remote storage settings:
// ===============================
// Provide all necessary credentials and configuration for accessing your AMAZON S3 storage
var s3Settings = new RemoteAttachmentsS3Settings
{
BucketName = "your-bucket-name",
AwsAccessKey = "your-amazon-access-key",
AwsSecretKey = "your-amazon-secret-key",
AwsRegionName = "your-region-name" // For example, "us-east-1"
RemoteFolderName = "your-s3-folder", // Optional
};
// Provide the necessary details for your AZURE Storage container
var azureSettings = new RemoteAttachmentsAzureSettings
{
StorageContainer = "your-azure-container-name",
AccountName = "your-azure-account-name",
AccountKey = "your-azure-account-key",
RemoteFolderName = "your-azure-folder" // Optional
};
// Define the remote attachments configuration:
// ============================================
var configuration = new RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration
{
// Add the remote storage destinations to the configuration
Destinations = new Dictionary<string, RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration>
{
{
// Provide a custom identifier for this remote destination (case-insensitive)
"my-amazon-storage",
new RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration
{
S3Settings = s3Settings, // The Amazon S3 settings
Disabled = false // Set to 'true' to disable this destination only
}
},
{
// Provide a custom identifier for this remote destination
"my-azure-storage",
new RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration
{
AzureSettings = azureSettings, // The Azure Storage settings
Disabled = false // Set to 'true' to disable this destination only
}
}
},
// OPTIONAL settings to control the remote attachments feature and its background task:
// Set to 'true' to disable the entire remote attachments feature
Disabled = false,
// The time interval (in seconds) between background task runs
CheckFrequencyInSec = 600,
// The maximum number of attachments processed in a single background task run
MaxItemsToProcess = 25,
// The maximum number of attachments that can be uploaded to remote storage concurrently
ConcurrentUploads = 6
};
// Apply the remote attachments configuration to the server:
// =========================================================
// This operation will override any existing remote attachment configurations on the server.
// Ensure all necessary destinations and settings are included in this configuration.
store.Maintenance.Send(new ConfigureRemoteAttachmentsOperation(configuration));
// Define remote storage settings:
// ===============================
// Provide all necessary credentials and configuration for accessing your AMAZON S3 storage
var s3Settings = new RemoteAttachmentsS3Settings
{
BucketName = "your-bucket-name",
AwsAccessKey = "your-amazon-access-key",
AwsSecretKey = "your-amazon-secret-key",
AwsRegionName = "your-region-name" // For example, "us-east-1"
RemoteFolderName = "your-s3-folder", // Optional
};
// Provide the necessary details for your AZURE Storage container
var azureSettings = new RemoteAttachmentsAzureSettings
{
StorageContainer = "your-azure-container-name",
AccountName = "your-azure-account-name",
AccountKey = "your-azure-account-key",
RemoteFolderName = "your-azure-folder" // Optional
};
// Define the remote attachments configuration:
// ============================================
var configuration = new RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration
{
// Add the remote storage destinations to the configuration
Destinations = new Dictionary<string, RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration>
{
{
// Provide a custom identifier for this remote destination (case-insensitive)
"my-amazon-storage",
new RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration
{
S3Settings = s3Settings, // The Amazon S3 settings
Disabled = false // Set to 'true' to disable this destination only
}
},
{
// Provide a custom identifier for this remote destination
"my-azure-storage",
new RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration
{
AzureSettings = azureSettings, // The Azure Storage settings
Disabled = false // Set to 'true' to disable this destination only
}
}
},
// OPTIONAL settings to control the remote attachments feature and its background task:
// Set to 'true' to disable the entire remote attachments feature
Disabled = false,
// The time interval (in seconds) between background task runs
CheckFrequencyInSec = 600,
// The maximum number of attachments processed in a single background task run
MaxItemsToProcess = 25,
// The maximum number of attachments that can be uploaded to remote storage concurrently
ConcurrentUploads = 6
};
// Apply the remote attachments configuration to the server:
// =========================================================
// This operation will override any existing remote attachment configurations on the server.
// Ensure all necessary destinations and settings are included in this configuration.
await store.Maintenance.SendAsync(new ConfigureRemoteAttachmentsOperation(configuration));
Get remote attachments settings
Use the GetRemoteAttachmentsConfigurationOperation to retrieve the current remote attachment settings.
- Sync
- Async
// Get the current remote attachments settings
RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration configuration = store.Maintenance.Send(
new GetRemoteAttachmentsConfigurationOperation());
// Display current settings
if (configuration != null)
{
// Time interval between task runs (seconds)
var checkFreqInSec = configuration.CheckFrequencyInSec;
// Number of concurrent uploads
var concurrentUploads = configuration.ConcurrentUploads;
foreach (var destination in configuration.Destinations)
{
// Destination identifier
var destinationId = destination.Key;
if (destination.Value.S3Settings != null)
{
// S3 bucket name
var s3BucketName = destination.Value.S3Settings.BucketName;
}
if (destination.Value.AzureSettings != null)
{
// Azure container name
var azureContainer = destination.Value.AzureSettings.StorageContainer;
}
}
}
else
{
// No remote attachments configuration found
}
// Get the current remote attachments settings asynchronously
RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration configuration = await store.Maintenance.SendAsync(
new GetRemoteAttachmentsConfigurationOperation());
// Display current settings
if (configuration != null)
{
// Time interval between task runs (seconds)
var checkFreqInSec = configuration.CheckFrequencyInSec;
// Number of concurrent uploads
var concurrentUploads = configuration.ConcurrentUploads;
foreach (var destination in configuration.Destinations)
{
// Destination identifier
var destinationId = destination.Key;
if (destination.Value.S3Settings != null)
{
// S3 bucket name
var s3BucketName = destination.Value.S3Settings.BucketName;
}
if (destination.Value.AzureSettings != null)
{
// Azure container name
var azureContainer = destination.Value.AzureSettings.StorageContainer;
}
}
}
else
{
// No remote attachments configuration found
}
Syntax
ConfigureRemoteAttachmentsOperation
// Configure the remote attachments settings using a store operation
public ConfigureRemoteAttachmentsOperation(RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration configuration)
GetRemoteAttachmentsConfigurationOperation
// Get the current remote attachments settings using a store operation
public GetRemoteAttachmentsConfigurationOperation
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| configuration | RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration | The remote attachments configuration class. |
RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration
public class RemoteAttachmentsConfiguration
{
// A dictionary of remote storage destinations, where each key is the destination identifier
public Dictionary<string, RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration> Destinations { get; set; }
// The time interval (in seconds) between background task runs
// Default: 60 seconds
public long? CheckFrequencyInSec { get; set; }
// The maximum number of attachments processed in a single background task run
// Default: int.MaxValue (unlimited)
public long? MaxItemsToProcess { get; set; }
// The maximum number of attachments that can be uploaded to remote storage concurrently
// Default: 8 attachments
public int? ConcurrentUploads { get; set; }
// Set to 'true' to disable the entire remote attachments feature
// Default: false
public bool Disabled { get; set; }
}
RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration
public class RemoteAttachmentsDestinationConfiguration
{
// Set to 'true' to disable this destination only
public bool Disabled { get; set; }
// Amazon S3 settings for the remote storage destination
public RemoteAttachmentsS3Settings S3Settings { get; set; }
// Azure Blob Storage settings for the remote storage destination
public RemoteAttachmentsAzureSettings AzureSettings { get; set; }
}
RemoteAttachmentsS3Settings
public class RemoteAttachmentsS3Settings
{
public string AwsAccessKey { get; set; }
public string AwsSecretKey { get; set; }
public string AwsSessionToken { get; set; }
public string AwsRegionName { get; set; }
public string BucketName { get; set; }
public string RemoteFolderName { get; set; }
public string CustomServerUrl { get; set; }
public bool ForcePathStyle { get; set; }
public S3StorageClass? StorageClass { get; set; }
}
RemoteAttachmentsAzureSettings
public class RemoteAttachmentsAzureSettings
{
public string StorageContainer { get; set; }
public string RemoteFolderName { get; set; }
public string AccountName { get; set; }
public string AccountKey { get; set; }
public string SasToken { get; set; }
}
S3StorageClass
public class S3StorageClass
{
// Default class for frequently accessed data with high durability and low latency.
public string Standard { get; set; }
For infrequently accessed, long-lived data; cheaper storage, retrieval fees apply.
public string StandardInfrequentAccess { get; set; }
// Similar to Standard-IA but stored in one availability zone;
// less resilient to failures but more cost-efficient.
public string OneZoneInfrequentAccess { get; set; }
// Automatically optimizes costs by moving data between access tiers.
public string IntelligentTiering { get; set; }
// Low-cost storage for archives; fast retrieval with retrieval fees.
public string GlacierInstantRetrieval { get; set; }
// Cheaper archival class; retrieval takes minutes to hours,
// suitable for data that doesn’t need immediate access.
public string Glacier { get; set; }
// Lowest-cost storage for rarely accessed data; retrieval may take hours.
public string DeepArchive { get; set; }
// Cheaper storage with lower durability, suitable for non-critical data.
public string ReducedRedundancy { get; set; }
// Faster access to objects stored in only one availability zone.
public string ExpressOneZone { get; set; }
}