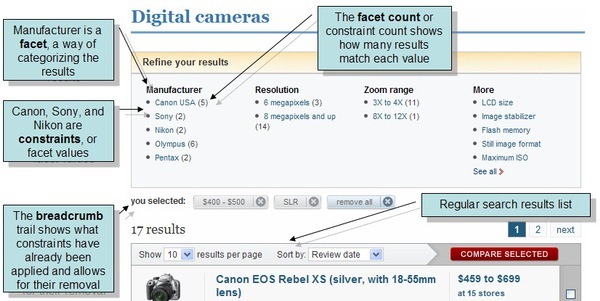
Query by Facets
-
A Faceted Search provides an efficient way to explore and navigate through large datasets or search results.
-
Multiple filters (facets) are applied to narrow down the search results according to different attributes or categories.
Define an index
-
To make a faceted search, a static-index must be defined for the fields you want to query and apply facets on.
-
The examples in this article will be based on the following Class, Index, and Sample Data:
- Class
- Index
- Sample_data
public class Camera
{
public string Manufacturer { get; set; }
public double Cost { get; set; }
public double MegaPixels { get; set; }
public int MaxFocalLength { get; set; }
public int UnitsInStock { get; set; }
}
public class Cameras_ByFeatures : AbstractIndexCreationTask<Camera>
{
public class IndexEntry
{
public string Brand { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public double MegaPixels { get; set; }
public int MaxFocalLength { get; set; }
public int UnitsInStock { get; set; }
}
public Cameras_ByFeatures()
{
Map = cameras => from camera in cameras
select new
{
Brand = camera.Manufacturer,
Price = camera.Cost,
MegaPixels = camera.MegaPixels,
MaxFocalLength = camera.MaxFocalLength,
UnitsInStock = camera.UnitsInStock
};
}
}
// Creating sample data for the examples in this article:
// ======================================================
var cameras = new[]
{
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Sony", Cost = 100, MegaPixels = 20.1, MaxFocalLength = 200, UnitsInStock = 10 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Sony", Cost = 200, MegaPixels = 29, MaxFocalLength = 250, UnitsInStock = 15 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Nikon", Cost = 120, MegaPixels = 22.3, MaxFocalLength = 300, UnitsInStock = 2 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Nikon", Cost = 180, MegaPixels = 32, MaxFocalLength = 300, UnitsInStock = 5 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Nikon", Cost = 220, MegaPixels = 40, MaxFocalLength = 300, UnitsInStock = 20 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Canon", Cost = 200, MegaPixels = 30.4, MaxFocalLength = 400, UnitsInStock = 30 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Olympus", Cost = 250, MegaPixels = 32.5, MaxFocalLength = 600, UnitsInStock = 4 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Olympus", Cost = 390, MegaPixels = 40, MaxFocalLength = 600, UnitsInStock = 6 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Fuji", Cost = 410, MegaPixels = 45, MaxFocalLength = 700, UnitsInStock = 1 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Fuji", Cost = 590, MegaPixels = 45, MaxFocalLength = 700, UnitsInStock = 5 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Fuji", Cost = 650, MegaPixels = 61, MaxFocalLength = 800, UnitsInStock = 17 },
new Camera { Manufacturer = "Fuji", Cost = 850, MegaPixels = 102, MaxFocalLength = 800, UnitsInStock = 19 }
};
using (var session = store.OpenSession())
{
foreach (var camera in cameras)
{
session.Store(camera);
}
session.SaveChanges();
}
Facets - Basics
Facets definition:
-
Define a list of facets by which to aggregate the data.
-
There are two Facet types:
Facet- returns a count for each unique term found in the specified index-field.RangeFacet- returns a count per range within the specified index-field.
// Define a list of facets to query by:
// ====================================
List<FacetBase> facets = new List<FacetBase>
{
// Define a Facet:
// ===============
new Facet
{
// Specify the index-field for which to get count of documents per unique ITEM
// e.g. get the number of Camera documents for each unique Brand
FieldName = "Brand",
// Set a display name for this field in the results (optional)
DisplayFieldName = "Camera Brand"
},
// Define a RangeFacet:
// ====================
new RangeFacet<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry>
{
Ranges =
{
// Specify ranges within an index-field in order to get count per RANGE
// e.g. get the number of Camera documents that cost below 200, between 200 & 400, etc...
x => x.Price < 200,
x => x.Price >= 200 && x.Price < 400,
x => x.Price >= 400 && x.Price < 600,
x => x.Price >= 600 && x.Price < 800,
x => x.Price >= 800
},
// Set a display name for this field in the results (optional)
DisplayFieldName = "Camera Price"
}
};
Query the index for facets results:
-
Query the index to get the aggregated facets information.
-
Either:
-
Pass the facets definition from above directly to the query
-
Or - construct a facet using a builder with the Fluent API option, as shown below.
-
- Query
- Query_async
- DocumentQuery
- Query_FluentAPI
- RawQuery
- RQL
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facets)
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = await asyncSession
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facets)
.ExecuteAsync();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
.DocumentQuery<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facets)
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Use a builder as follows:
.AggregateBy(builder => builder
// Specify the index-field (e.g. 'Brand') for which to get count per unique ITEM
.ByField(x => x.Brand)
// Set a display name for the field in the results (optional)
.WithDisplayName("Camera Brand"))
.AndAggregateBy(builder => builder
// Specify ranges within an index field (e.g. 'Price') in order to get count per RANGE
.ByRanges(
x => x.Price < 200,
x => x.Price >= 200 && x.Price < 400,
x => x.Price >= 400 && x.Price < 600,
x => x.Price >= 600 && x.Price < 800,
x => x.Price >= 800)
// Set a display name for the field in the results (optional)
.WithDisplayName("Camera Price"))
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
// Provide the RQL string to the RawQuery method
.RawQuery<Camera>(@"from index 'Cameras/ByFeatures'
select
facet(Brand) as 'Camera Brand',
facet(Price < 200.0,
Price >= 200.0 and Price < 400.0,
Price >= 400.0 and Price < 600.0,
Price >= 600.0 and Price < 800.0,
Price >= 800.0) as 'Camera Price'")
// Execute the query
.ExecuteAggregation();
from index "Cameras/ByFeatures"
select
facet(Brand) as "Camera Brand",
facet(Price < 200.0,
Price >= 200.0 and Price < 400.0,
Price >= 400.0 and Price < 600.0,
Price >= 600.0 and Price < 800.0,
Price >= 800.0) as "Camera Price"
Query results:
-
Query results are Not the collection documents, they are of type:
Dictionary<string, FacetResult>which is the facets results per index-field specified. -
Using the sample data from this article, the resulting aggregations will be:
// The resulting aggregations per display name will contain:
// =========================================================
// For the "Camera Brand" Facet:
// "canon" - Count: 1
// "fuji" - Count: 4
// "nikon" - Count: 3
// "olympus" - Count: 2
// "sony" - Count: 2
// For the "Camera Price" Ranges:
// "Price < 200" - Count: 3
// "Price >= 200.0 and Price < 400.0" - Count: 5
// "Price >= 400.0 and Price < 600.0" - Count: 2
// "Price >= 600.0 and Price < 800.0" - Count: 1
// "Price >= 800.0" - Count: 1
// Get facets results for index-field 'Brand' using the display name specified:
// ============================================================================
var brandFacets = results["Camera Brand"];
var numberOfBrands = brandFacets.Values.Count; // 5 unique brands
// Get the aggregated facet value for a specific Brand:
var facetValue = brandFacets.Values[0];
// The brand name is available in the 'Range' property
// Note: value is lower-case since the default RavenDB analyzer was used by the index
Assert.Equal("canon", facetValue.Range);
// Number of documents for 'Canon' is available in the 'Count' property
Assert.Equal(1, facetValue.Count);
// Get facets results for index-field 'Price' using the display name specified:
// ============================================================================
var priceFacets = results["Camera Price"];
var numberOfRanges = priceFacets.Values.Count; // 5 different ranges
// Get the aggregated facet value for a specific Range:
facetValue = priceFacets.Values[0];
Assert.Equal("Price < 200", facetValue.Range); // The range string
Assert.Equal(3, facetValue.Count); // Number of documents in this range
Query further:
-
Typically, after presenting users with the initial facets results which show the available options,
users can select specific categories to explore further. -
For example, if the user selects Fuji and Nikon,
then your next query can include a filter to focus only on those selected brands.
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> filteredResults = session
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Limit query results to the selected brands:
.Where(x => x.Brand.In("Fuji", "Nikon"))
.AggregateBy(facets)
.Execute();
Facets - Options
Facets definition:
-
Options are available only for the
Facettype. -
Available options:
Start- The position from which to send items (how many to skip).PageSize- Number of items to return.IncludeRemainingTerms- Show summary of items that didn't make it into the requested PageSize.TermSortMode- Set the sort order on the resulting items.
// Define the list of facets to query by:
// ======================================
List<FacetBase> facetsWithOptions = new List<FacetBase>
{
// Define a Facet:
new Facet
{
// Specify the index-field for which to get count of documents per unique ITEM
FieldName = "Brand",
// Set some facets options
Options = new FacetOptions
{
// Return the top 3 brands with most items count:
PageSize = 3,
TermSortMode = FacetTermSortMode.CountDesc
}
}
};
Query the index for facets results:
- Query
- Query_async
- DocumentQuery
- Query_FluentAPI
- RawQuery
- RQL
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facetsWithOptions)
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = await asyncSession
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facetsWithOptions)
.ExecuteAsync();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
.DocumentQuery<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facetsWithOptions)
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Use a builder as follows:
.AggregateBy(builder => builder
// Specify an index-field (e.g. 'Brand') for which to get count per unique ITEM
.ByField(x => x.Brand)
// Specify the facets options
.WithOptions(new FacetOptions
{
// Return the top 3 brands with most items count:
PageSize = 3,
TermSortMode = FacetTermSortMode.CountDesc
}))
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
// Provide the RQL string to the RawQuery method
.RawQuery<Camera>(@"from index 'Cameras/ByFeatures'
select facet(Brand, $p0)")
// Add the facet options to the "p0" parameter
.AddParameter("p0", new { PageSize = 3, TermSortMode = FacetTermSortMode.CountDesc })
// Execute the query
.ExecuteAggregation();
from index "Cameras/ByFeatures"
select facet(Brand, $p0)
{"p0": { "TermSortMode": "CountDesc", "PageSize": 3 }}
Query results:
// The resulting items will contain:
// =================================
// For the "Brand" Facet:
// "fuji" - Count: 4
// "nikon" - Count: 3
// "olympus" - Count: 2
// As requested, only 3 unique items are returned, ordered by documents count descending:
// Get facets results for index-field 'Brand':
// ===========================================
var brandFacets = results["Brand"];
var numberOfBrands = brandFacets.Values.Count; // 3 brands
// Get the aggregated facet value for a specific Brand:
var facetValue = brandFacets.Values[0];
// The brand name is available in the 'Range' property
// Note: value is lower-case since the default RavenDB analyzer was used by the index
Assert.Equal("fuji", facetValue.Range);
// Number of documents for 'Fuji' is available in the 'Count' property
Assert.Equal(4, facetValue.Count);
Facets - Aggregations
Facets definition:
-
Aggregation of data is available for an index-field per unique Facet or Range item.
For example:- Get the total number of UnitsInStock per Brand
- Get the highest MegaPixels value for documents that cost between 200 & 400
-
The following aggregation operations are available:
- Sum
- Average
- Min
- Max
-
Multiple operations can be added on each facet, for multiple fields.
// Define the list of facets to query by:
// ======================================
List<FacetBase> facetsWithAggregations = new List<FacetBase>
{
// Define a Facet:
// ===============
new Facet
{
FieldName = "Brand",
Aggregations =
{
{
// Set the aggregation operation:
FacetAggregation.Sum,
// Create a HasSet specifying the index-fields for which to perform the aggregation
new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get total number of UnitsInStock per Brand
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "UnitsInStock"}
}
},
{
FacetAggregation.Average, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get average Price per Brand
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "Price"}
}
},
{
FacetAggregation.Min, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get min Price per Brand
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "Price"}
}
},
{
FacetAggregation.Max, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get max MegaPixels per Brand
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "MegaPixels"},
// Get max MaxFocalLength per Brand
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "MaxFocalLength"}
}
}
}
},
// Define a RangeFacet:
// ====================
new RangeFacet<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry>
{
Ranges =
{
x => x.Price < 200,
x => x.Price >= 200 && x.Price < 400,
x => x.Price >= 400 && x.Price < 600,
x => x.Price >= 600 && x.Price < 800,
x => x.Price >= 800
},
Aggregations =
{
{
FacetAggregation.Sum, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get total number of UnitsInStock for each group of documents per range specified
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "UnitsInStock"}
}
},
{
FacetAggregation.Average, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get average Price of each group of documents per range specified
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "Price"}
}
},
{
FacetAggregation.Min, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get min Price of each group of documents per range specified
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "Price"}
}
},
{
FacetAggregation.Max, new HashSet<FacetAggregationField>
{
// Get max MegaPixels for each group of documents per range specified
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "MegaPixels"},
// Get max MaxFocalLength for each group of documents per range specified
new FacetAggregationField {Name = "MaxFocalLength"}
}
}
}
}
};
Query the index for facets results:
- Query
- Query_async
- DocumentQuery
- Query_FluentAPI
- RawQuery
- RQL
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facetsWithAggregations)
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = await asyncSession
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facetsWithAggregations)
.ExecuteAsync();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
.DocumentQuery<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Pass the defined facets from above
.AggregateBy(facetsWithAggregations)
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateBy' to aggregate the data by facets
// Use a builder as follows:
.AggregateBy(builder => builder
// Specify an index-field (e.g. 'Brand') for which to get count per unique ITEM
.ByField(x => x.Brand)
// Specify the aggregations per the Brand facet:
.SumOn(x => x.UnitsInStock)
.AverageOn(x => x.Price)
.MinOn(x => x.Price)
.MaxOn(x => x.MegaPixels)
.MaxOn(x => x.MaxFocalLength))
.AndAggregateBy(builder => builder
// Specify ranges within an index field (e.g. 'Price') in order to get count per RANGE
.ByRanges(
x => x.Price < 200,
x => x.Price >= 200 && x.Price < 400,
x => x.Price >= 400 && x.Price < 600,
x => x.Price >= 600 && x.Price < 800,
x => x.Price >= 800)
// Specify the aggregations per the Price range:
.SumOn(x => x.UnitsInStock)
.AverageOn(x => x.Price)
.MinOn(x => x.Price)
.MaxOn(x => x.MegaPixels)
.MaxOn(x => x.MaxFocalLength))
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
// Provide the RQL string to the RawQuery method
.RawQuery<Camera>(@"from index 'Cameras/ByFeatures'
select
facet(Brand,
sum(UnitsInStock),
avg(Price),
min(Price),
max(MegaPixels),
max(MaxFocalLength)),
facet(Price < $p0,
Price >= $p1 and Price < $p2,
Price >= $p3 and Price < $p4,
Price >= $p5 and Price < $p6,
Price >= $p7,
sum(UnitsInStock),
avg(Price),
min(Price),
max(MegaPixels),
max(MaxFocalLength))")
// Add the parameters' values
.AddParameter("p0", 200.0)
.AddParameter("p1", 200.0)
.AddParameter("p2", 400.0)
.AddParameter("p3", 400.0)
.AddParameter("p4", 600.0)
.AddParameter("p5", 600.0)
.AddParameter("p6", 800.0)
.AddParameter("p7", 800.0)
// Execute the query
.ExecuteAggregation();
from index "Cameras/ByFeatures"
select
facet(Brand,
sum(UnitsInStock),
avg(Price),
min(Price),
max(MegaPixels),
max(MaxFocalLength)),
facet(Price < $p0,
Price >= $p1 and Price < $p2,
Price >= $p3 and Price < $p4,
Price >= $p5 and Price < $p6,
Price >= $p7,
sum(UnitsInStock),
avg(Price),
min(Price),
max(MegaPixels),
max(MaxFocalLength))
{"p0":200.0,"p1":200.0,"p2":400.0,"p3":400.0,"p4":600.0,"p5":600.0,"p6":800.0,"p7":800.0}
Query results:
// The resulting items will contain (Showing partial results):
// ===========================================================
// For the "Brand" Facet:
// "canon" Count:1, Sum: 30, Name: UnitsInStock
// "canon" Count:1, Min: 200, Average: 200, Name: Price
// "canon" Count:1, Max: 30.4, Name: MegaPixels
// "canon" Count:1, Max: 400, Name: MaxFocalLength
//
// "fuji" Count:4, Sum: 42, Name: UnitsInStock
// "fuji" Count:4, Min: 410, Name: Price
// "fuji" Count:4, Max: 102, Name: MegaPixels
// "fuji" Count:4, Max: 800, Name: MaxFocalLength
//
// etc.....
// For the "Price" Ranges:
// "Price < 200.0" Count:3, Sum: 17, Name: UnitsInStock
// "Price < 200.0" Count:3, Min: 100, Average: 133.33, Name: Price
// "Price < 200.0" Count:3, Max: 32, Name: MegaPixels
// "Price < 200.0" Count:3, Max: 300, Name: MaxFocalLength
//
// "Price < 200.0 and Price > 400.0" Count:5, Sum: 75, Name: UnitsInStock
// "Price < 200.0 and Price > 400.0" Count:5, Min: 200, Average: 252, Name: Price
// "Price < 200.0 and Price > 400.0" Count:5, Max: 40, Name: MegaPixels
// "Price < 200.0 and Price > 400.0" Count:5, Max: 600, Name: MaxFocalLength
//
// etc.....
// Get results for the 'Brand' Facets:
// ==========================================
var brandFacets = results["Brand"];
// Get the aggregated facet value for a specific Brand:
var facetValue = brandFacets.Values[0];
// The brand name is available in the 'Range' property:
Assert.Equal("canon", facetValue.Range);
// The index-field on which aggregation was done is in the 'Name' property:
Assert.Equal("UnitsInStock", facetValue.Name);
// The requested aggregation result:
Assert.Equal(30, facetValue.Sum);
// Get results for the 'Price' RangeFacets:
// =======================================
var priceRangeFacets = results["Price"];
// Get the aggregated facet value for a specific Brand:
facetValue = priceRangeFacets.Values[0];
// The range string is available in the 'Range' property:
Assert.Equal("Price < 200.0", facetValue.Range);
// The index-field on which aggregation was done is in the 'Name' property:
Assert.Equal("UnitsInStock", facetValue.Name);
// The requested aggregation result:
Assert.Equal(17, facetValue.Sum);
Storing facets definition in a document
Define and store facets in a document:
-
The facets definitions can be stored in a document.
-
That document can then be used by a faceted search query.
// Create a FacetSetup object:
// ===========================
FacetSetup facetSetup = new FacetSetup
{
// Provide the ID of the document in which the facet setup will be stored.
// This is optional -
// if not provided then the session will assign an ID for the stored document.
Id = "customDocumentID",
// Define Facets and RangeFacets to query by:
Facets = new List<Facet> {
new Facet()
{
FieldName = "Brand"
}},
RangeFacets = new List<RangeFacet>
{
new RangeFacet<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry>
{
Ranges =
{
x => x.MegaPixels < 20,
x => x.MegaPixels >= 20 && x.MegaPixels < 30,
x => x.MegaPixels >= 30 && x.MegaPixels < 50,
x => x.MegaPixels >= 50
}
}
}
};
// Store the facet setup document and save changes:
// ================================================
session.Store(facetSetup);
session.SaveChanges();
// The document will be stored under the 'FacetSetups' collection
Query using facets from document:
- Query
- Query_async
- DocumentQuery
- RawQuery
- RQL
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateUsing'
// Pass the ID of the document that contains your facets setup
.AggregateUsing("customDocumentID")
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = await asyncSession
// Query the index
.Query<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateUsing'
// Pass the ID of the document that contains your facets setup
.AggregateUsing("customDocumentID")
.ExecuteAsync();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
.DocumentQuery<Cameras_ByFeatures.IndexEntry, Cameras_ByFeatures>()
// Call 'AggregateUsing'
// Pass the ID of the document that contains your facets setup
.AggregateUsing("customDocumentID")
.Execute();
Dictionary<string, FacetResult> results = session.Advanced
// Query the index
// Provide the RQL string to the RawQuery method
.RawQuery<Camera>(@"from index 'Cameras/ByFeatures'
select facet(id('customDocumentID'))")
// Execute the query
.ExecuteAggregation();
from index "Cameras/ByFeatures"
select facet(id("customDocumentID"))
Syntax
IAggregationQuery<T> AggregateBy<T>(FacetBase facet);
IAggregationQuery<T> AggregateBy<T>(IEnumerable<FacetBase> facets);
IAggregationQuery<T> AggregateBy<T>(Action<IFacetBuilder<T>> builder);
IAggregationQuery<T> AggregateUsing<T>(string facetSetupDocumentKey);
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| facet | FacetBase | FacetBase implementation defining the facet and its options.Either Facet or RangeFacet. |
| facets | IEnumerable<FacetBase> | Enumerable containing FacetBase implementations. |
| builder | Action<IFacetFactory<T>> | Builder with a fluent API that constructs a FacetBase instance. |
| facetSetupDocumentId | string | ID of a document containing FacetSetup. |
- Facet
- RangeFacet
- FacetBase
- FacetAggregation
public class Facet
{
public string FieldName { get; set; }
public FacetOptions Options { get; set; }
}
public class Facet<T>
{
public Expression<Func<T, object>> FieldName { get; set; }
public FacetOptions Options { get; set; }
}
public class RangeFacet
{
public List<string> Ranges { get; set; }
}
public class RangeFacet<T>
{
public List<Expression<Func<T, bool>>> Ranges { get; set; }
}
public class FacetBase
{
public Dictionary<FacetAggregation, HashSet<FacetAggregationField>> Aggregations { get; set; }
public string DisplayFieldName { get; set; }
}
public enum FacetAggregation
{
None,
Max,
Min,
Average,
Sum
}
Fluent API builder methods:
IFacetOperations<T> ByField(string fieldName);
IFacetOperations<T> ByField(Expression<Func<T, object>> path);
IFacetOperations<T> ByRanges(Expression<Func<T, bool>> path, params Expression<Func<T, bool>>[] paths);
IFacetOperations<T> WithDisplayName(string displayName);
IFacetOperations<T> WithOptions(FacetOptions options);
IFacetOperations<T> SumOn(Expression<Func<T, object>> path);
IFacetOperations<T> MinOn(Expression<Func<T, object>> path);
IFacetOperations<T> MaxOn(Expression<Func<T, object>> path);
IFacetOperations<T> AverageOn(Expression<Func<T, object>> path);
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fieldName | string | The index-field to use for the facet |
| path | Expression<Func<T, bool>> | Points to the index-field to use for the facet (ByRanges, ByField) or for the aggregation (SumOn, MinOn, MaxOn, AverageOn) |
| displayName | string | If set, results of a facet will be returned under this name |
| options | FacetOptions | Non-default options to use in the facet definition |
Options:
public class FacetOptions
{
public FacetTermSortMode TermSortMode { get; set; } = FacetTermSortMode.ValueAsc;
public bool IncludeRemainingTerms { get; set; }
public int Start { get; set; }
public int PageSize { get; set; } = int.MaxValue;
}
| Option | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TermSortMode | FacetTermSortMode | Set the sort order on the resulting items ( ValueAsc (Default), ValueDesc, CountAsc, CountDesc) |
| Start | int | The position from which to send items (how many to skip) |
| PageSize | int | Number of items to return |
| IncludeRemainingTerms | bool | Indicates if remaining terms that didn't make it into the requested PageSize should be included in results |